RBF (Gaussian) Kernel Modelを使うためのWrapper Classを作りました
分類問題において,非線形な決定境界を表現するための一つの方法に,RBF Kernel Modelがあります. これは,入力$latex x$を以下で定義される$latex \phi(x)$に変換するものです.
コードはGistに載せてあります:
https://gist.github.com/nkt1546789/e41199340f7a42c515be
使い方は,例えばsklearnのLogisticRegressionに適用したい場合は,
clf=RbfModelWrapper(LogisticRegression()).fit(X,y)同様にRidgeに適用したい場合は,
clf=RbfModelWrapper(Ridge()).fit(X,y)ちなみにGridSearchもできるようになっています:
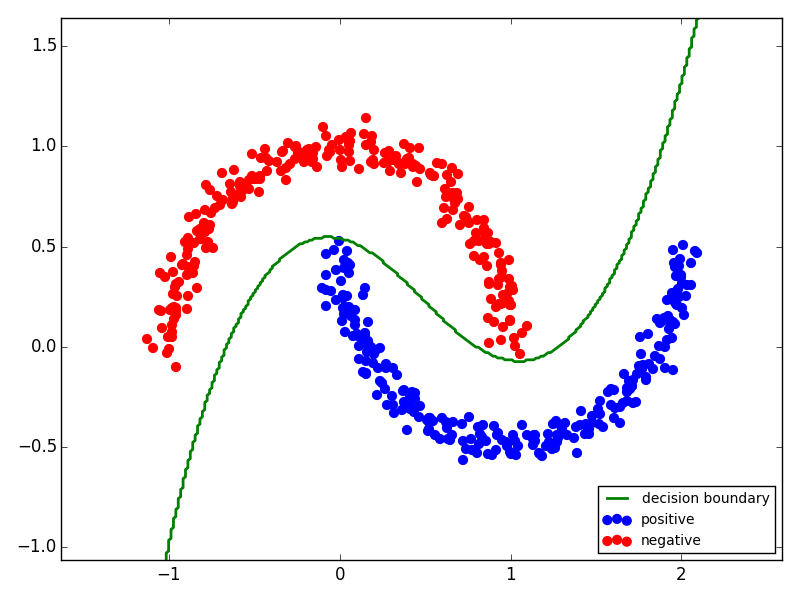
gs=GridSearchCV(RbfModelWrapper(Ridge()),param_grid={"gamma":np.logspace(-2,0,9),"alpha":[1,10,100]}).fit(X[itr],y[itr])とりあえずデモとして,2moonsを分類してみました:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(1)
n=500
X,y=datasets.make_moons(n_samples=n,noise=.05)
idx=np.random.permutation(n)
ntr=np.int32(n*0.7)
itr=idx[:ntr]
ite=idx[ntr:]
param_grid={"gamma":np.logspace(-2,0,9)}
grid=GridSearchCV(RbfModelWrapper(LogisticRegression()),param_grid=param_grid)
grid.fit(X[itr],y[itr])
clf=grid.best_estimator_
print "accuracy:",clf.score(X[ite],y[ite])
offset=.5
xx,yy=np.meshgrid(np.linspace(X[:,0].min()-offset,X[:,0].max()+offset,300),
np.linspace(X[:,1].min()-offset,X[:,1].max()+offset,300))
Z=clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()])
Z=Z.reshape(xx.shape)
a=plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0.5], linewidths=2, colors='green')
b1=plt.scatter(X[y==1][:,0],X[y==1][:,1],color="blue",s=40)
b2=plt.scatter(X[y==0][:,0],X[y==0][:,1],color="red",s=40)
plt.axis("tight")
plt.xlim((X[:,0].min()-offset,X[:,0].max()+offset))
plt.ylim((X[:,1].min()-offset,X[:,1].max()+offset))
plt.legend([a.collections[0],b1,b2],
[r"decision boundary","positive","unlabeled"],
prop={"size":10},loc="lower right")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()以下のように100%の精度で分類出来ました: